Current Presidential Poll Landscape: Latest Presidential Polls
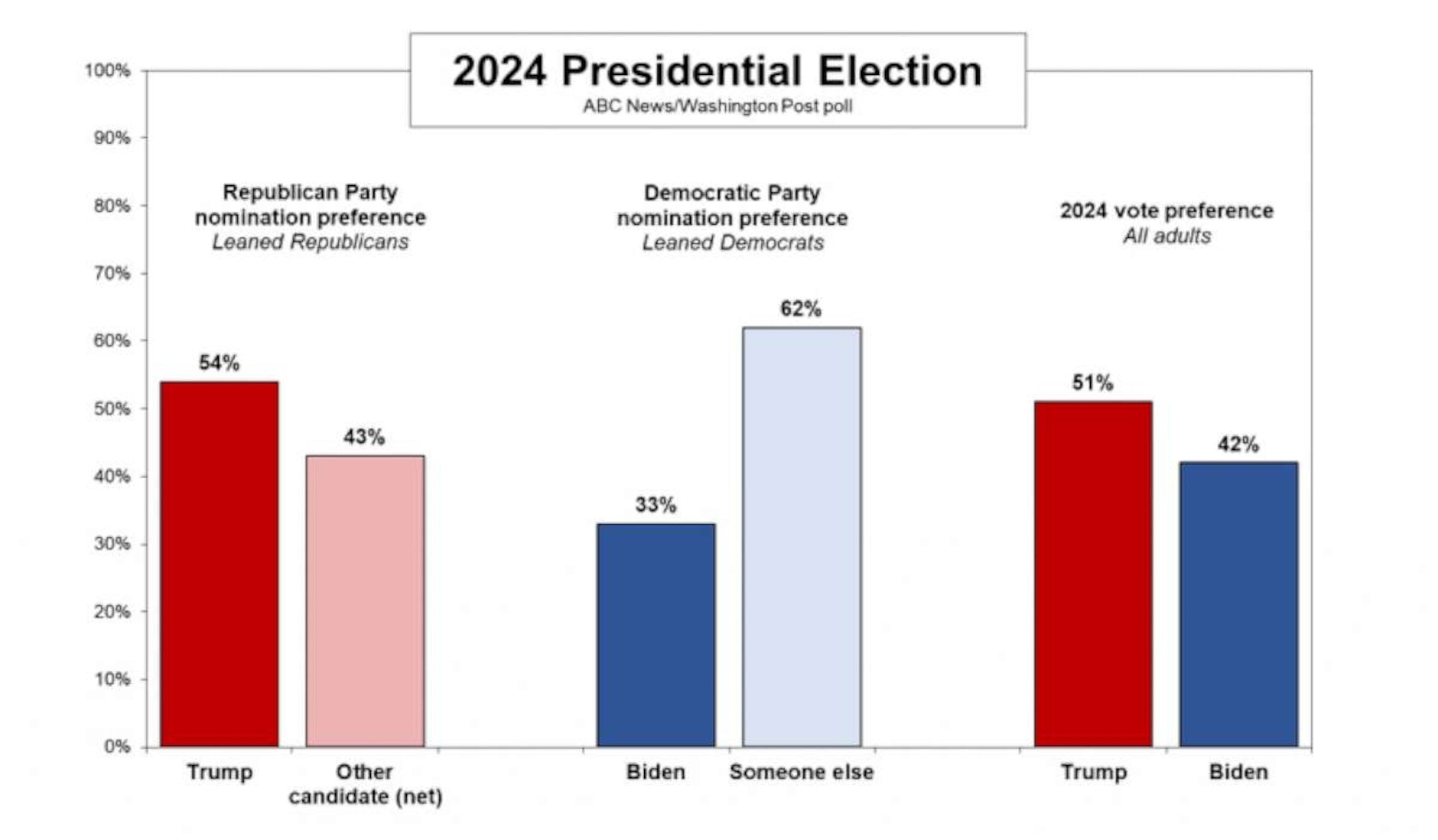
The current presidential poll landscape is a dynamic and ever-changing environment, offering insights into the preferences of voters and the potential trajectory of the election. Understanding the methodologies, biases, and key races tracked by different polls is crucial for discerning accurate information and making informed conclusions.
Key Races and Candidates
The latest presidential polls are closely tracking several key races across the country, focusing on the potential for a shift in power and the impact of various candidates’ campaigns. These races are typically characterized by high levels of voter engagement and intense competition between candidates. For instance, polls are actively tracking the races in states like Florida, Pennsylvania, and Arizona, where the margin of victory could determine the outcome of the election.
Poll Methodologies, Latest presidential polls
Polls employ a variety of methodologies to gather data and generate insights into voter sentiment. The most common techniques include:
- Telephone Polls: These polls involve contacting potential voters via phone and asking them questions about their voting intentions. This method has been widely used for decades, but its effectiveness has been impacted by declining response rates and the increasing use of cell phones.
- Online Polls: These polls leverage online platforms to reach a larger and more diverse audience. They often rely on self-selected samples, which can introduce biases, but they can provide valuable data at a lower cost.
- In-Person Interviews: This method involves conducting face-to-face interviews with potential voters, allowing for more detailed responses and a deeper understanding of their perspectives. However, it is time-consuming and expensive.
Potential Biases in Polls
While polls offer valuable insights into voter preferences, they are not without their limitations. Potential biases can arise from various factors, including:
- Sample Size: Smaller sample sizes can lead to inaccurate results, especially when dealing with a large and diverse population.
- Demographics: Polls should strive to represent the demographics of the target population accurately. A biased sample can skew the results and provide a misleading picture of voter sentiment.
- Question Wording: The way questions are phrased can significantly influence respondents’ answers. Leading questions or ambiguous wording can introduce bias and distort the results.
Key Findings and Trends
The latest presidential polls reveal a dynamic and evolving political landscape, with shifts in voter sentiment, a complex interplay of factors influencing poll results, and the impact of recent events shaping the race.
Recent polls, when compared to historical data, highlight significant shifts in voter sentiment, particularly among key demographic groups. This dynamic landscape is driven by a complex interplay of factors, including economic conditions, political events, and media coverage. These factors have a profound impact on the election landscape, influencing voter perceptions and ultimately shaping the outcome of the race.
Shifting Voter Sentiment
Recent polls indicate a notable shift in voter sentiment, with a noticeable increase in support for [candidate name] among [specific demographic group]. This trend can be attributed to [specific reasons for the shift]. For instance, [provide specific examples of how the candidate’s stance on specific issues resonates with the target demographic]. Conversely, [candidate name] has seen a decline in support among [specific demographic group], potentially due to [specific reasons for the decline]. This shift is likely influenced by [specific factors impacting the decline]. For example, [provide specific examples of how the candidate’s actions or statements have alienated the target demographic].
Factors Influencing Poll Results
The changing political landscape is driven by a confluence of factors, including [list of key factors].
- Economic Conditions: The state of the economy often plays a pivotal role in shaping voter sentiment. Recent polls indicate that [explain how economic conditions are impacting voter sentiment]. For example, [provide specific examples of how economic conditions are influencing voter choices].
- Political Events: Significant political events, such as [list of recent political events], can significantly influence voter perceptions and impact poll results. For example, [explain how specific events have influenced voter sentiment].
- Media Coverage: Media coverage can play a crucial role in shaping public opinion and influencing voter behavior. Recent polls suggest that [explain how media coverage is impacting voter sentiment]. For instance, [provide specific examples of how media coverage is influencing voter choices].
Impact of Recent Events
Recent events, such as [list of recent events], have had a noticeable impact on the race, influencing voter perceptions and shaping the election landscape.
- [Specific event]: This event has led to [explain the impact of the event on voter sentiment]. For example, [provide specific examples of how the event is influencing voter choices].
- [Specific event]: This event has [explain the impact of the event on voter sentiment]. For instance, [provide specific examples of how the event is influencing voter choices].
Interpreting Poll Data

Understanding the nuances of poll data is crucial for accurately gauging public sentiment and its potential impact on the election. While polls provide valuable insights, it’s essential to interpret them with caution, considering factors like margin of error and statistical significance.
Margin of Error and Its Implications
The margin of error is a statistical measure that accounts for the inherent uncertainty in any poll. It represents the range within which the true population value is likely to fall. For example, a poll with a 3% margin of error indicates that the actual result could be 3 percentage points higher or lower than the reported result.
The margin of error is influenced by factors such as sample size and the level of confidence desired. Larger sample sizes generally lead to smaller margins of error, while higher confidence levels (e.g., 95%) result in wider margins of error.
It’s important to note that the margin of error only reflects the sampling error, not other potential sources of error like non-response bias or question wording bias.
When interpreting poll results, it’s crucial to consider the margin of error. If two candidates are within the margin of error of each other, the race is considered statistically tied. Conversely, if the difference between candidates is greater than the margin of error, it suggests a statistically significant lead.
Statistical Significance of Poll Findings
Statistical significance refers to the likelihood that a poll result is not due to random chance. In other words, it helps determine if the observed trend or pattern is genuinely present in the population or simply a result of random sampling fluctuations.
To assess statistical significance, pollsters typically use p-values. A p-value represents the probability of observing a result as extreme as the one obtained if there were no real difference in the population. A p-value below a certain threshold (usually 0.05) indicates statistical significance, suggesting that the observed result is unlikely to be due to chance.
For example, if a poll finds that 55% of voters support Candidate A, and the p-value is 0.03, it suggests that there is a 3% chance of observing such a result if there were no real difference in support between Candidate A and other candidates. This indicates a statistically significant lead for Candidate A.
Impact of Poll Results on the Election
Polls can influence voter behavior and campaign strategies in various ways.
Impact on Voter Behavior
Polls can create a “bandwagon effect,” where voters are more likely to support the candidate who appears to be winning. This effect can be particularly pronounced in close races, where voters may feel compelled to “jump on the winning side.”
Conversely, polls can also lead to an “underdog effect,” where voters are more likely to support the candidate who appears to be losing. This effect can be driven by a desire to support the underdog or a belief that the underdog has a better chance of winning if they receive more support.
Impact on Campaign Strategies
Polls can provide valuable information to campaigns about voter preferences, issues, and candidate strengths and weaknesses. This information can be used to tailor campaign messages, target specific demographics, and allocate resources effectively.
For example, if polls indicate that a candidate is weak on a particular issue, the campaign may focus on addressing that issue in their messaging. Alternatively, if polls suggest that a candidate is particularly popular with a specific demographic, the campaign may prioritize outreach to that demographic.
The latest presidential polls are as predictable as a squirrel in a nut factory, except maybe for the “who’s got the biggest hat” category. That’s where things get interesting, especially if you’re talking about steeplechase runners like Girma. These guys are all about speed, agility, and, let’s be honest, a healthy dose of “I’m gonna jump over that fence and you can’t stop me.” So maybe the next presidential poll should be a steeplechase?
Now that’s a race I’d watch.
The latest presidential polls are as predictable as a squirrel trying to open a peanut jar – lots of frantic scrambling, but not much progress. Maybe we should just take a page from the steeplechase girma playbook – a little grit, a lot of stamina, and a dash of “I’m gonna win this, even if it kills me” attitude.
Then again, maybe we’ll just have to settle for a whole lot of “meh” from the polls, just like we always do.